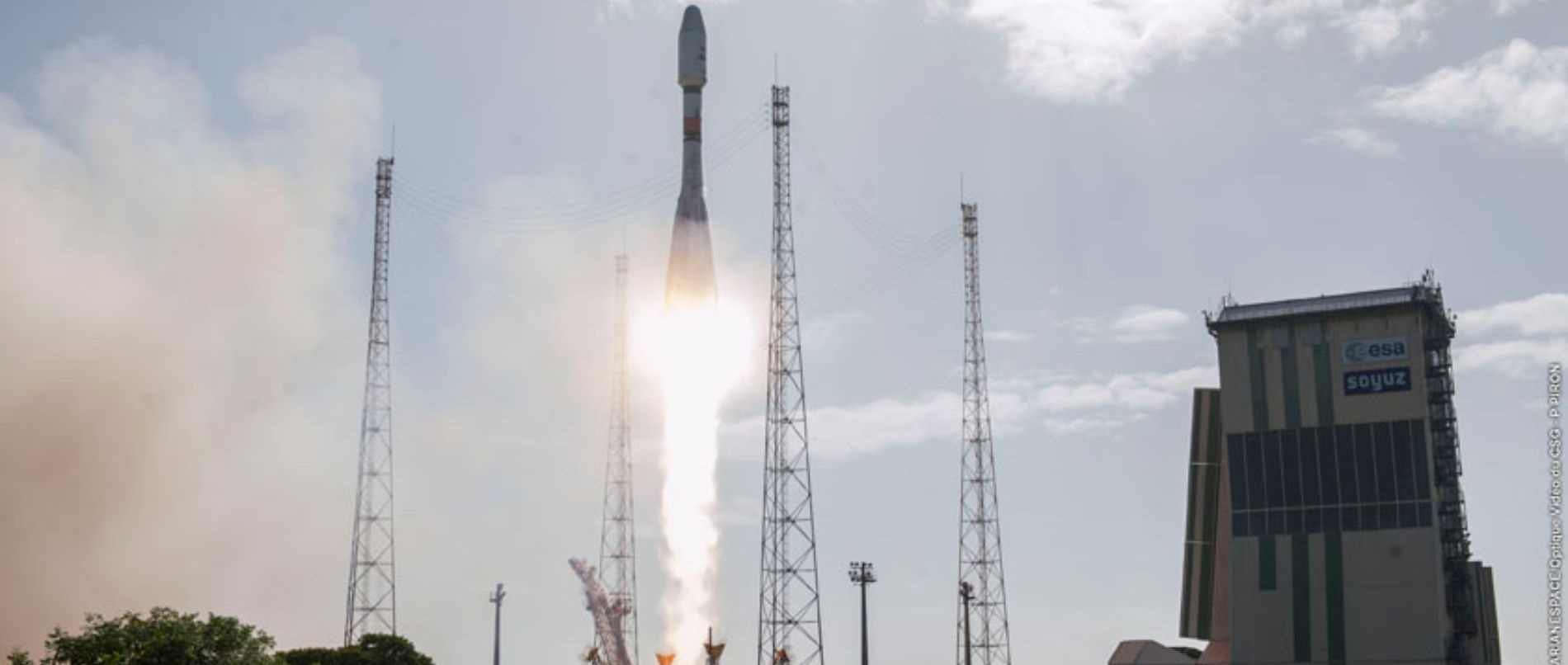
A “Europeanized” Soyuz rocket will launch from the Guiana Space Center with the third set of O3b satellites joining a constellation of telecommunications satellites placed into an 8,063-Kilometer orbit above the equator to deliver low-latency data services to the developing world. O3b stands for “the other three billion” in reference to the world’s population that can not connect to the Internet through conventional means; it is operated by O3b Networks, a wholly owned subsidiary of SES S.A. Outfitted with a Fregat upper stage, Soyuz will directly deliver the four 700-Kilogram satellites into their checkout orbit over the equator.
 |
|
Launch date:
|
March 9, 2018
Instantaneous Launch Window:
|
- WASHINGTON, D.C. 11:37:06 A.M.
- KOUROU, FRENCH GUIANA 1:37:06 P.M.
- UNIVERSAL TIME (UTC) 16:37:06
- LUXEMBOURG AND PARIS 5:37:06 P.M.
Launch site:
|
ELS Guiana Space Center, Centre Spatial Guyanais, Kourou 97387, Französisch-Guyana
{colsp=2}
[highlight]L[eventtimer]2018-03-09 16:37:06;%c%%ddd%/%hh%:%mm%:%ss%[/eventtimer][/highlight]

Launch coverage:
Payload:
O3b FM-13, 14, 15, 16
The O3b satellites lofted by Arianespace Flight VS18 are the 54th, 55th, 56th and 57th satellites to be launched by Arianespace for the global satellite operator SES.
SES is the world-leading satellite operator and the first to deliver a differentiated and scalable GEO-MEO offering worldwide, with more than 50 satellites in Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) and 12 in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO). SES focuses on value-added, end-to-end solutions in two key business units: SES Video and SES Networks. The company provides satellite communications services to broadcasters, content and internet service providers, mobile and fixed network operators, governments and institutions. SES’s portfolio includes the ASTRA satellite system, which has the largest Direct-to-Home (DTH) television reach in Europe; O3b, a global managed data communications service provider; and MX1, a leading media service provider that offers a full suite of innovative digital video and media services.
Positioned at approximately 8,000 km., the O3b satellites are about four-times-closer to Earth than geostationary (GEO) satellites, and provide low-latency, fibre-like connectivity.
The new Ka-band satellites will join the existing O3b constellation to deliver high-speed connectivity to people and businesses in the growing mobility, fixed data and government markets. By scaling efficiently its MEO fleet, SES is adding 38% more capacity across the globe and growing the addressable market from 45 to 50 degrees north and south latitude.


The current 12-spacecraft constellation was orbited by Arianespace, utilizing its medium-lift Soyuz workhorse to carry four spacecraft each on launches that began in June 2013, and was followed by missions in July and December 2014.
The four O3b MEO satellites orbited on VS18 will enable SES Networks to offer more capacity, enhanced coverage, increased efficiencies and greater reliability while delivering carrier-grade services including MEF Carrier Ethernet 2.0 certified services to telecommunications operators, mobile network operators (MNOs), enterprises, Internet service providers (ISPs) and government customers.
SES will be launching another four O3b MEO satellites for the constellation with Arianespace in 2019. In addition, Arianespace also has one SES geostationary satellite in its order book.
The O3b satellites on Flight VS18 were built by Thales Alenia Space in its plant in Cannes, France. They are the 151st to 154th satellites from this manufacturer to be launched by Arianespace.
Eleven other Thales Alenia Space-built satellites are in Arianespace’s order book.
Specifications
Type / Application:|
- Communication
Operator:|
- O3b Networks Ltd.
Contractors:|
- Thales Alenia Space
Equipment:|
- 12 Ka-Band transponders
Configuration:|
Propulsion:|
- Hydrazine monopropellant
- 8 × 1 N thrusters
Power:|
- 2 deployable solar arrays
- batteries
Life Time:|
- 10 years
Launch Mass:|
- 700 kg
Orbit:|
- Perigee 7825 km (per Gunter's Space Page)/ 7830 km (per Arianespace Mission Press Kit)
- Inclination 0° (per Gunter's Space Page)/ 0.04° (per Arianespace Mission Press Kit)
Launch Vehicle:
Soyuz 2-1B is the next-generation of the Russian workhorse Soyuz Launcher. It is nearly identical to previously flown Soyuz launchers, but features an upgraded Control System switching from analog to digital control system to make the Soyuz Launcher more flexible and an upgraded third stage featuring the RD-0124 Engine. Soyuz 2-1B Rockets are being operated from the Baikonur Cosmodrome (LC-31), LC-43 at Plesetsk Cosmodrome and the Kourou Space Center in French Guiana. The Launcher is available to Russian Government Customers as well as commercial customers via the Arianespace affiliate Starsem that operated the Soyuz launcher.
With its new digital control system, Soyuz 2-1B can perform more flexible Ascent Missions. The old Soyuz Launchers had to be rotated on their launch tables to the correct launch azimuth angle since their control system was not able to perform a Roll Maneuver early in the flight. With the new digital control System, the launch table does not need to be rotated since the digital control system supports three-axis vehicle control from the point of liftoff. The digital controller also provides more stability during ascent, allowing the Soyuz to be outfitted with larger Payload Fairings enabling it to carry bigger payloads. The old Soyuz control system was unable to handle the instabilities caused by a larger fairing. In addition, the Soyuz 2 generation of vehicles provides a significantly higher injection accuracy that is important for direct-to-orbit flights. The Soyuz 2-1B has a higher payload capability than the Soyuz 2-1A that is using the conventional third stage design.



Soyuz 2-1B is usually outfitted with a Fregat Upper Stage that features its own autonomous control system that takes over after the Soyuz has released the Orbital Unit. Fregat provides more injection accuracy and is able to make several engine burns during the flight to allow payloads to be delivered to a variety of orbits including Low Earth Orbit, Sun-Synchronous Orbit, Geosynchronous transfer orbit and Geosynchronous Orbit. By launching from three Launch Sites around the Globe, Soyuz 2 can target a variety of orbital inclinations.
Soyuz 2 is manufactured by TsSKB-Progress of Samara, Russia.
Soyuz 2-1B Specifications
The Soyuz-2 Vehicle stands 46.1 meters tall and has a main diameter of 2.95 meters and a span of 10.3 meters from booster fin to booster fin.
All stages of the vehicle use Rocket Propellant 1 (Rocket-Grade Kerosene) and Liquid Oxygen as propellants. Liftoff mass is about 303,000 Kilograms, excluding payload and upper stage mass.
The 2-1B version of the Soyuz can deliver payloads of up to 7,800 Kilograms to Low Earth Orbit featuring a slightly improved performance over the previous Soyuz Vehicles, making it suitable for launches of heavy satellites targeting Low Earth Orbits.
With an appropriate Upper Stage like Fregat, Soyuz can reach a variety of orbits including Sun Synchronous, Medium Earth and Geostationary Transfer Orbit. Direct Geostationary Insertions and Escape Missions are also possible, primarily for small spacecraft.
Specifications
Manufacturer:|
- TSSKB-Progress
Height:|
- 46.1 m
Diameter:|
- 2.95 m
Launch Mass:|
- 303,000kg
Mass to LEO:|
- 7,800 kg
Mass to MEO:|
- 1,645 kg
Mass to GTO:|
- 3,250 kg
Mass to SSO:|
- 4,400 kg
Mass to GEO:|
- 1,440 kg
Flight Sequence/Launch Profile:
Refer to Press Kit.
L-1 Weather forecast for Kourou, French Guinea
Time
|
Temps
|
Humidity
|
Precipitation
|
Wind
|
Weather
5 p.m. (Based on hourly forecast with 1 hour interval and the closest to launch time)
|
5 p.m. (Based on hourly forecast with 1 hour interval and the closest to launch time)
28 °C (Feels like 32 °C)
|
72%
|
20 %
|
NE at 23 km/h
|
Mostly Cloudy
Links:
Last edited: